|
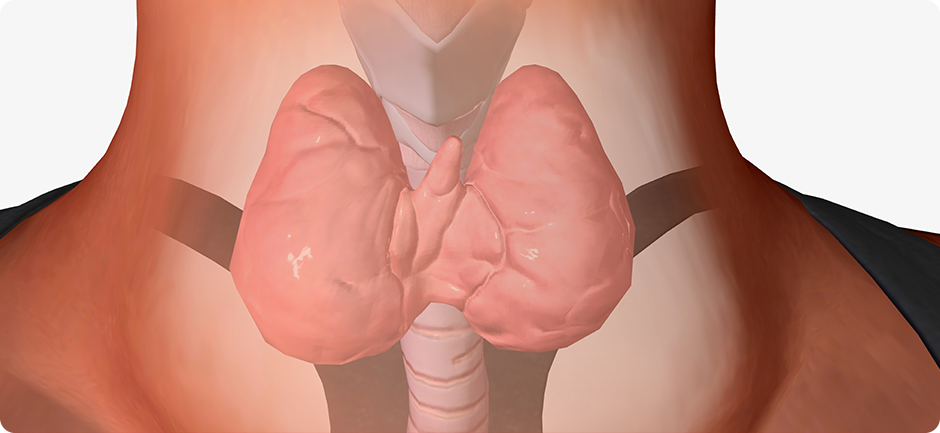
Thyroid Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland produces more thyroid hormones than the body needs. This excessive production accelerates many bodily functions and can cause symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, tremors, nervousness, excessive sweating, heat intolerance, insomnia, and unexplained weight loss. Many patients also report increased appetite, muscle weakness, fatigue, menstrual irregularities in women, and feelings of anxiety. In some cases, swelling in the neck (goiter) or eye problems may occur. The causes of hyperthyroidism vary. The most common is Graves’ disease, an autoimmune disorder that leads to overstimulation of the thyroid. Other causes include toxic adenoma, toxic multinodular goiter, and certain forms of thyroiditis that cause temporary hormone release. In some cases, it may result from excessive intake of thyroxine. Diagnosis is made through blood tests measuring hormone levels and specific antibodies, often complemented by thyroid ultrasound or scintigraphy for accurate assessment. Treatment choice depends on the cause, patient age, and overall health. Main treatment options include antithyroid medications, radioactive iodine, or surgical removal of the thyroid. Regular follow-up is essential to monitor treatment response and prevent complications such as hypothyroidism. At our clinic, we provide comprehensive and responsible care for managing hyperthyroidism. Respecting each patient’s needs, we utilize the most advanced diagnostic and therapeutic methods, aiming not only for hormonal balance but also for overall improvement in quality of life. Additionally, we offer guidance on diet and lifestyle to support patients at every stage of treatment, building a relationship of trust and meaningful care. |

|